
In other words, Na+ and Cl– ions are held together by electrovalent or ionic bond. So, Na + and Cl – ions being oppositely charged atoms which attract each other and are held by strong electrostatic forces of attraction to exist as NaCl. This makes chloride ion, Cl - as negatively charged. The nucleus of chlorine atom has 17 protons and the number of electrons become 18. On the other hand chlorine has seven electrons in its outer most shell and it require one more electron to complete its octet. Therefore, if becomes positively charged sodium ion or cation (Na +). The nucleus of this atom still has 11 protons but the number of electrons are 10.

If it loses an electron from its M shell then its L shell becomes the outermost shell. So they exist monoatomic, sodium atom has one electron in its outermost shell. Due to this stable configuration, the noble gases have no tendency to lose or gain electrons. It is clear from the above table that except helium, all other noble gases have 8 electrons (octet) in their outermost shell which represent a highly stable electronic configuration. The electronic configuration of noble gases and some metals and non-metals are given in the following table.Įlectronic Configuration of Some Elements Types of element The noble gases, which have a completely filled valence shell or outermost shell, are very stable. Each atom has a tendency to attain a completely filled valance shell. The combining power of an atom is expressed as valency. Long Tabular Form of the Reactivity SeriesĪtoms of elements combine to form stable molecules.

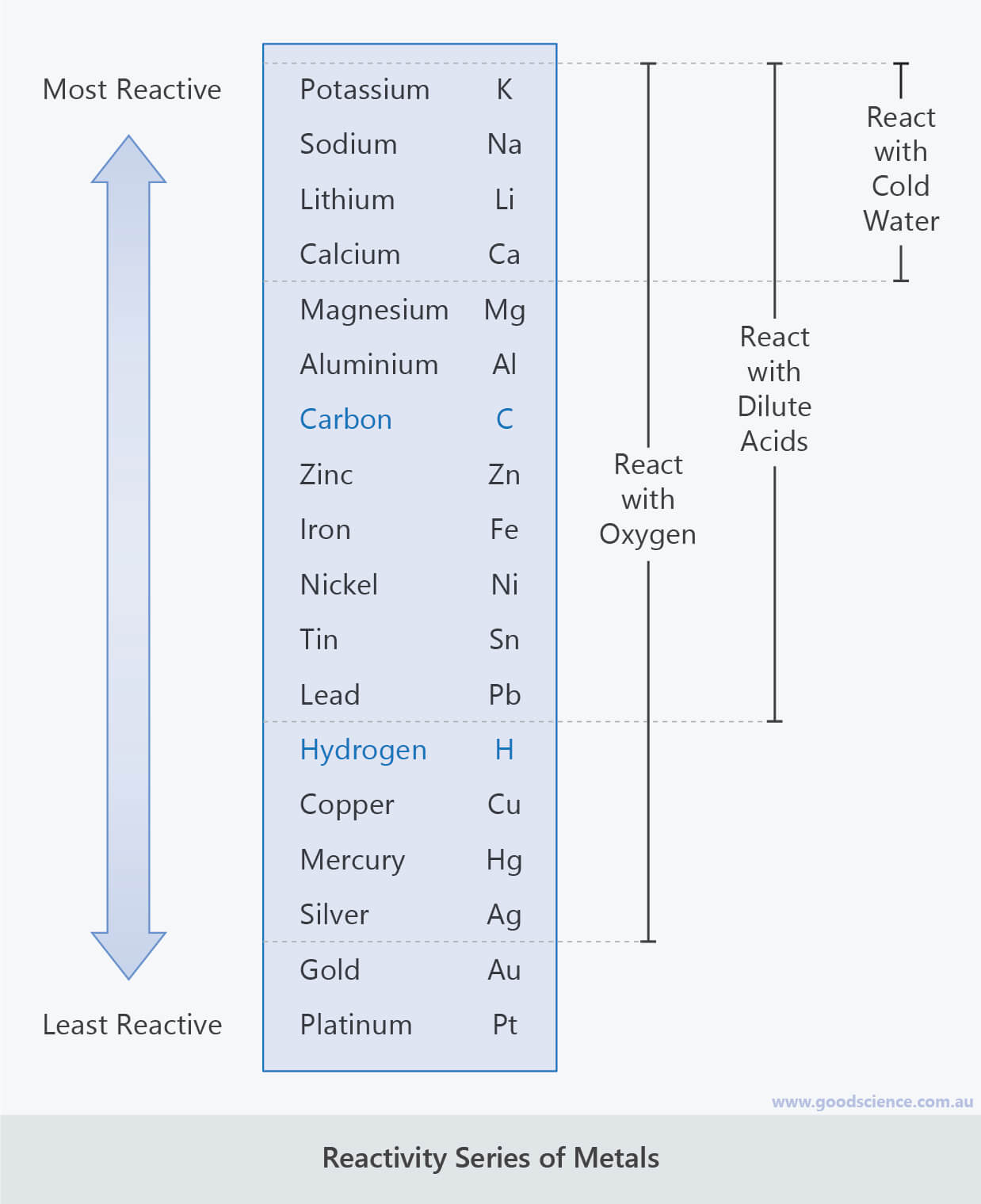
Due to hydrogen can also lose an electron and form positive ion (H +).It may be noted that hydrogen is not a metal but even then it has been placed in the reactivity series.In this table, the most reactive metal is placed above hydrogen and the less reactive metal is placed below hydrogen.
Metal ion reactivity series series#


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
